Device for monitoring the wakefulness of the driver
The device prevents the driver from falling asleep while driving. The device is equipped with an electronic unit that takes an electroencephalogram and an electromyogram in online mode and, when critical parameters are detected, it gives a sound warning.

Task
There is a cold hard statistics on accidents and disasters; however, some of the most terrible disasters and accidents of the recent past, caused by human fatigue and distraction, are rather more indicative.
Exxon Valdez ship wreck
When the Exxon Valdez tanker ran aground off the coast of Alaska in 1989, it caused the second largest oil spill in history. Before the departure, the management of the transport company decided to carry out a staff reduction. Those who stayed had to work on a 14-hour shift. One of the assistants to the captain fell asleep at the workplace and did not report on the location data on time. As a result, 11 million gallons of oil spilled into the open ocean.
Three Mile Island accident
The Three Mile Island nuclear accident: the reactor core began to melt at 4 am on March 28, 1979, followed by a leak and explosion. The investigation showed that all those on duty were asleep at the time of the accident and could not take appropriate safety measures.
Selby train wreck
The largest railway disaster occurred in the UK on February 28, 2001. The high-speed train went off the rails near the town of Selby due to the fact that the driver was asleep and did not slow down on the slope.
In this project, the task of the laboratory staff was to develop a device for detecting the process of the drivers’ falling asleep and early warning of the onset of a critical condition.
Solution
During the implementation of the project, a wearable device was developed that registers the user’s biometric parameters and recognizes the onset of their falling asleep. In this case, the biometry comprises the parameters of blinking, heart rate and EMG.
After the user puts on the device, individual average and critical parameter values for this user are determined. When a critical value in one or more parameters is reached, the device starts making loud noises to prevent the user from falling asleep.
User data for the entire trip are recorded in a mobile phone and then automatically or manually synchronized with the cloud. To work with the device, a special mobile application has been developed for tuning personal settings (response levels, tone volume, etc.)
Advantages of the solution:
- Reducing risks and losses due to the human factor in the work of the driver (operator)
- The ability to collect statistics on fatigue of workers in certain areas or segments.
Details
The project consists of two main parts: the development of a portable wireless device and the development of a set of algorithms to determine the functional state of the driver by physiological indicators, taken in real time. The wearable device is equipped with 5 worn on the forehead electrodes for measuring the electroencephalogram (EEG), electromyogram (EMG) and pulse wave, and an inertial sensor for measuring the parameters of the driver’s head movements. Pre-processing sensor data and determination of driver’s status is also carried out on the device. The complex of developed algorithms includes various algorithms that determine the state of the driver based on the data received from the device. At this stage of the work, an algorithm has been developed for determining the functional state of a person based on blinking parameters obtained from an EEG signal. At the moment, the device constructive proposals are being processed in order to obtain a form factor that allows the part of the device containing electrodes to be hidden under a hat. In the future, during the course of research tests, it is necessary to collect a new database for the development of a complex of algorithms based on an expanded number of indicators (EEG spectrum intensity, heart rate, head movement parameters).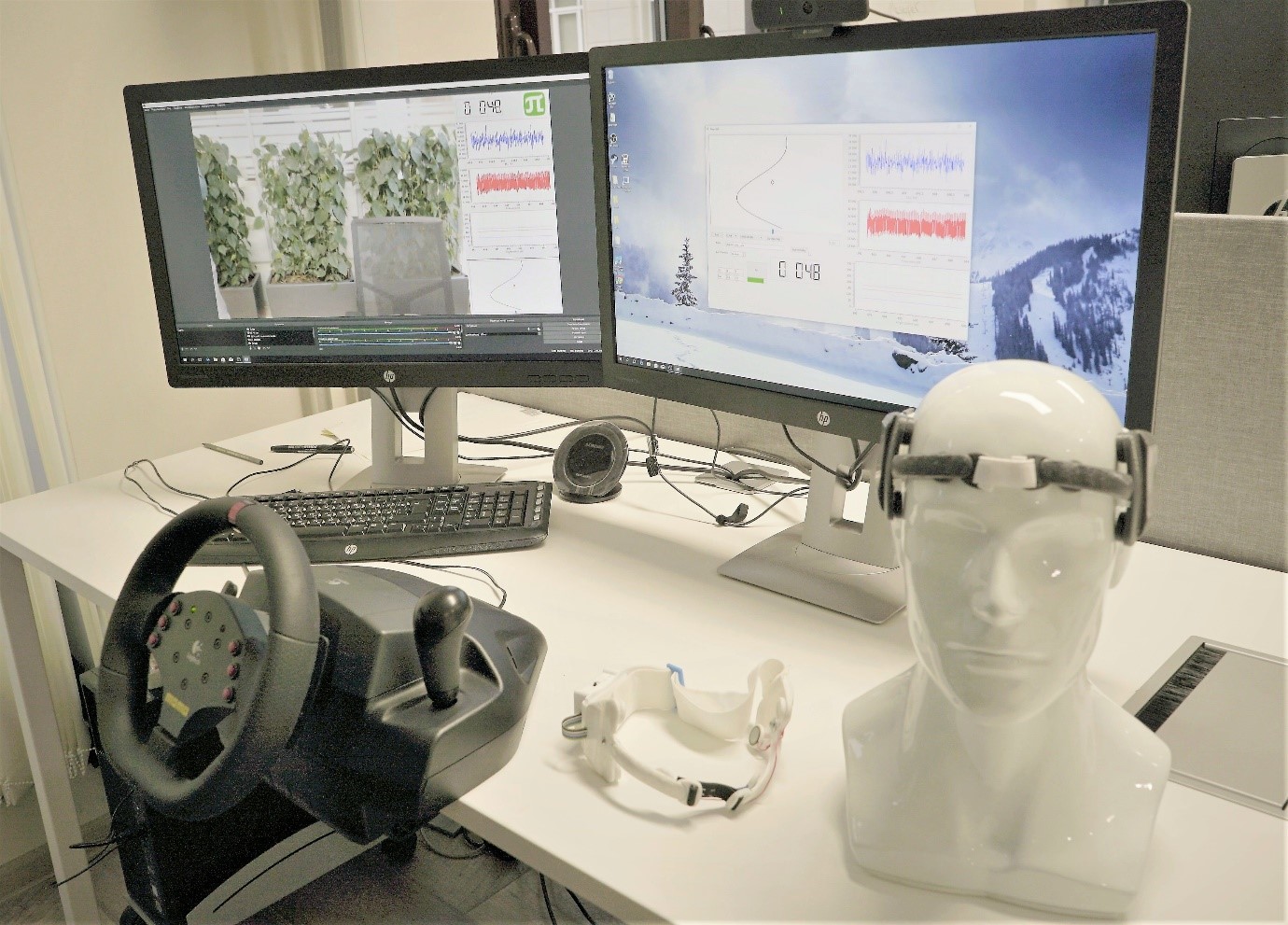
The research stand
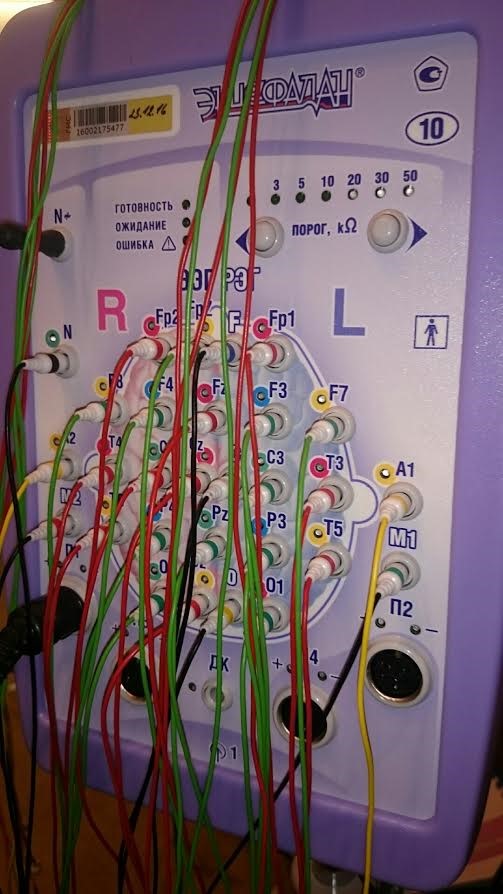

The Encephalan medical device with a reference signal
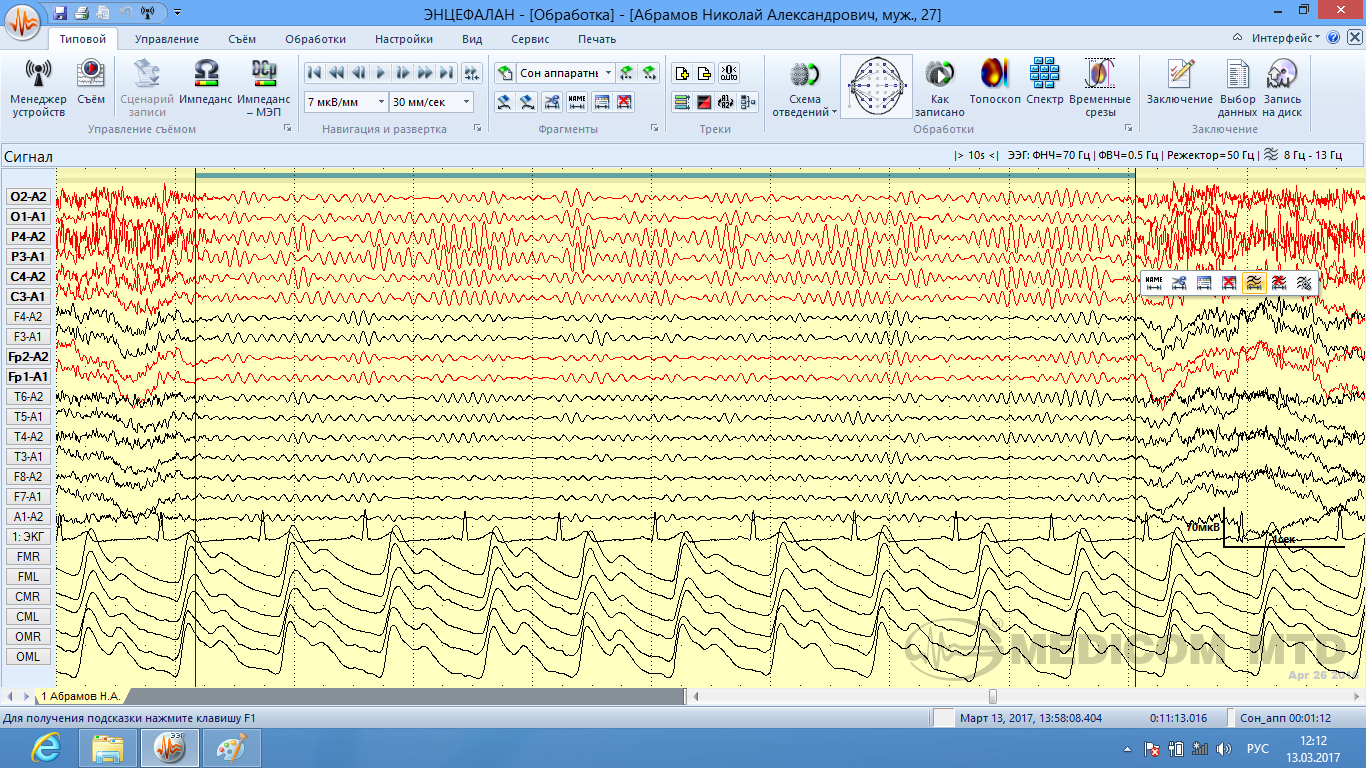
Example of the received EEG signal from the Encephalan medical device
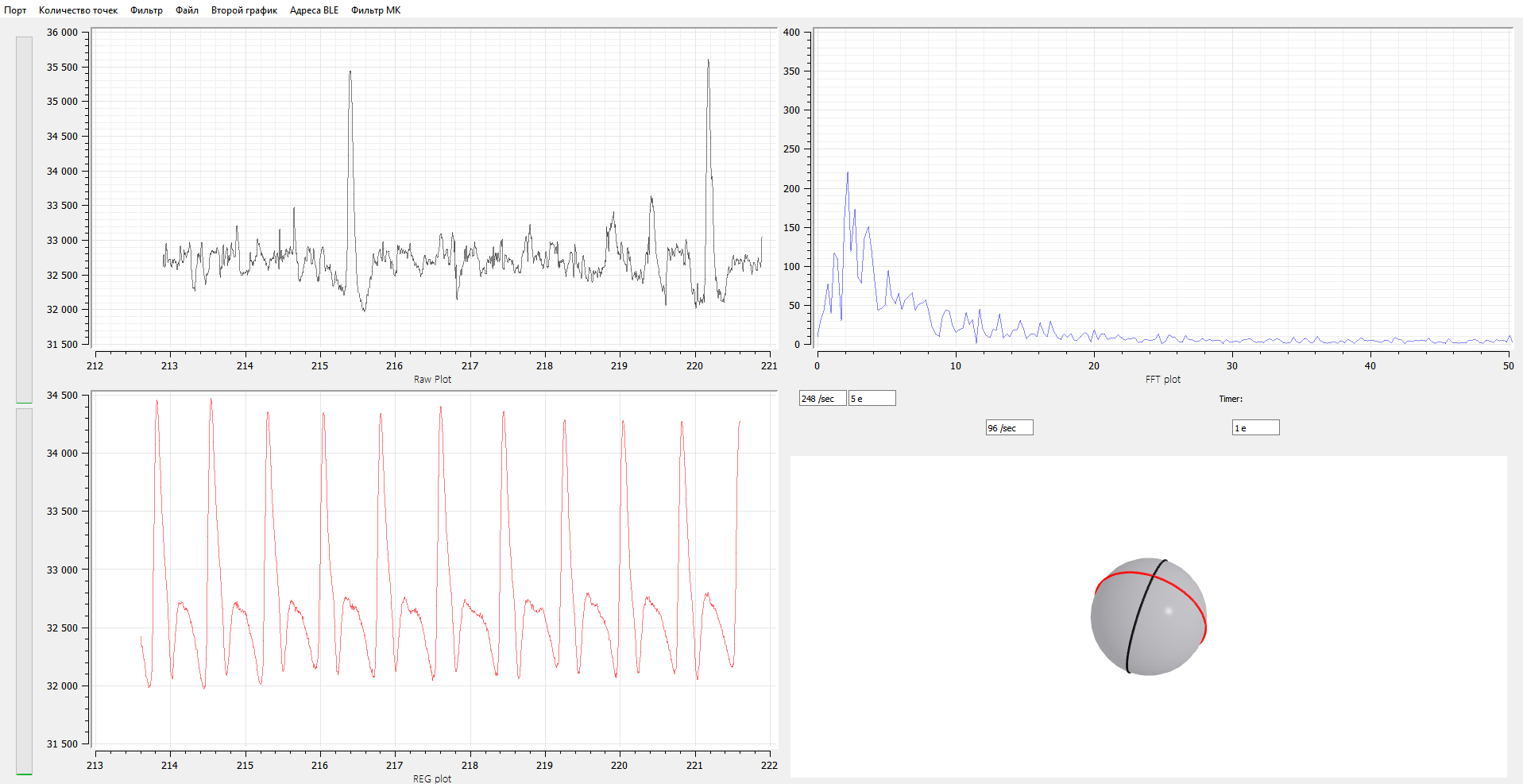
Example of the received signals (clear EEG, EEG spectrum, pulse wave, head position) from the device under development.
Technologies
| Programming languages and network | C, C++, Qt |
| Platforms | ARM |
| VCS | Git |
| IDE | IAR |
| Wireless technologies | Bluetooth 4.0 (BLE) |
| Microcontroller | STM32 |
Intellectual Property
Publications
Project team
- Project manager: A. Boykov
- Engineers: G. Vasilyanov, A. Vasilev