A virtual model of gas filling station pumps has been developed
The objective of the project is to provide students with the requisite training to enable them to operate the compressor and auxiliary equipment employed at a vehicle gas filling station.

The project has been carried out as part of the Education Quality Improvement and Personnel Training Programme (2022-2023) for Gazprom PJSC/Peter the Great St. Petersburg Polytechnic University (SPbPU). The project aims to optimize the educational process in disciplines relevant to Gazprom PJSC at the Higher School of Power Engineering of the Institute of Energy, SPbPU.
The terms of reference and lab session scenarios were developed at the Higher School of Power Engineering. 3D modeling and the software part were carried out by specialists from the Industrial Systems for Streaming Data Processing Laboratory of the SPbPU AES.
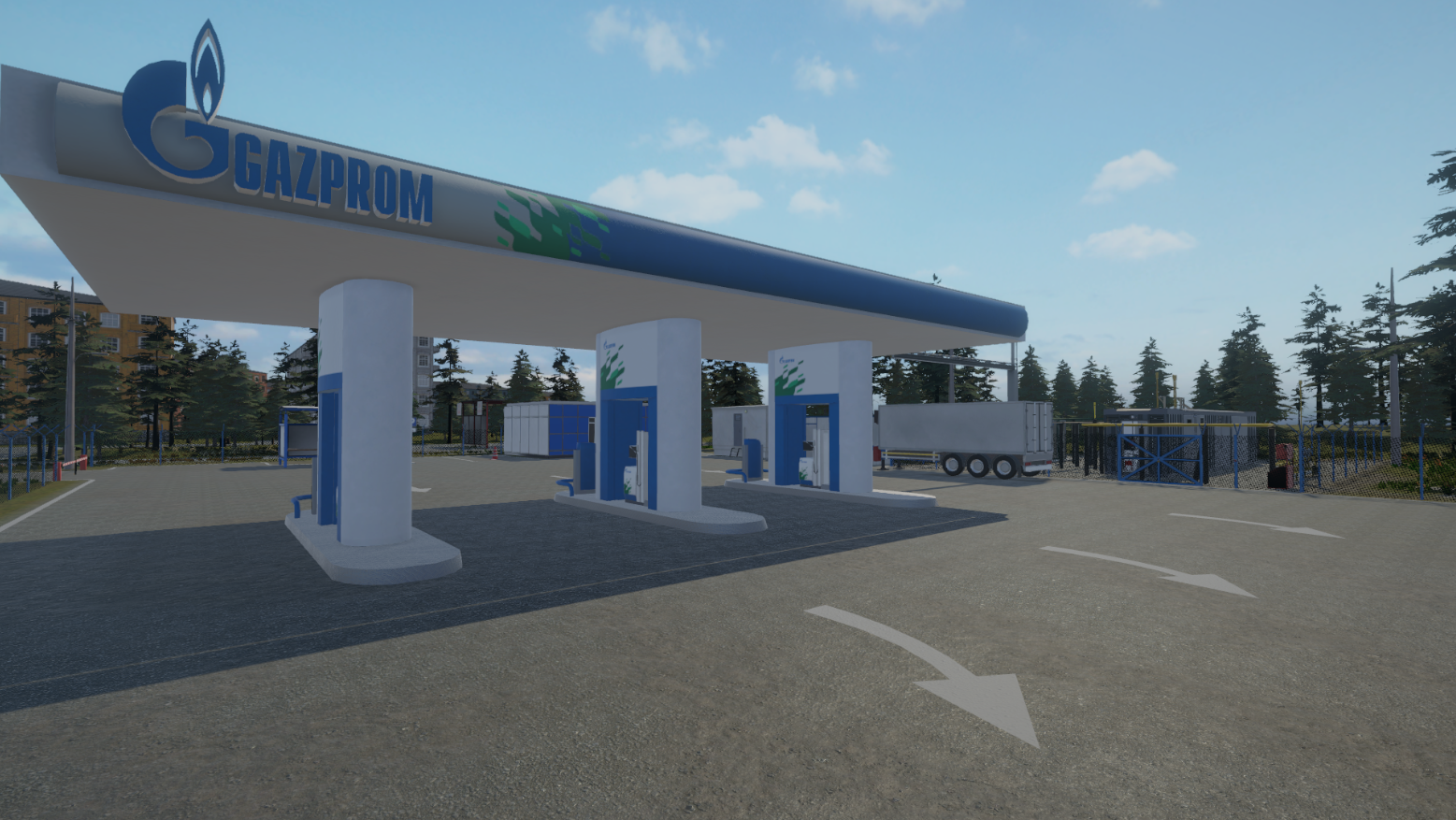
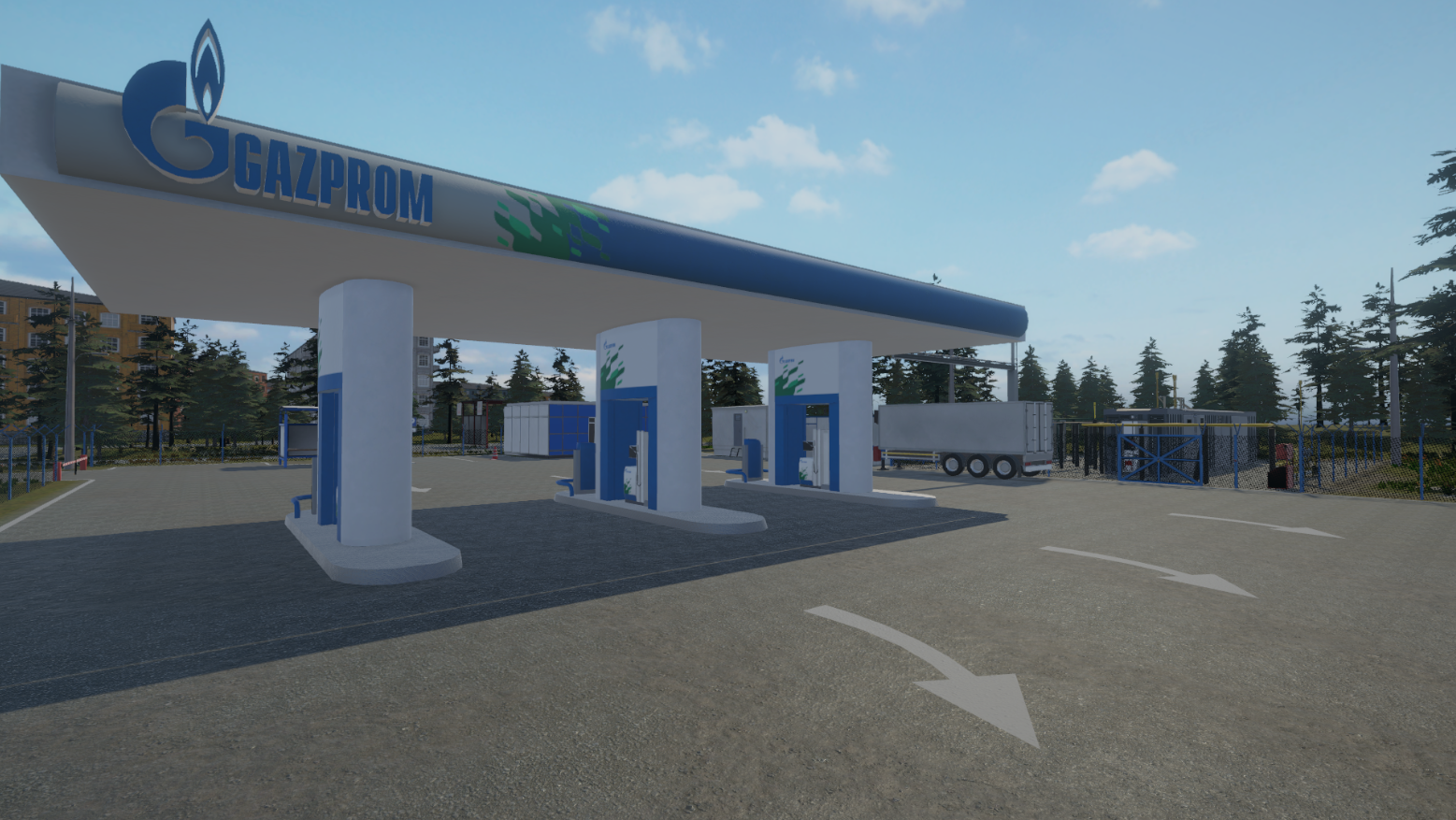
The virtual laboratory is a three-dimensional digital model of a compressed natural gas (CNG) filling station, equipped with interactive control tools and training scenarios.
CNG filling stations are a common type of compressor stations in the final part of the gas distribution system. The CNG filling stations are used to refuel CNG-fueled vehicles. The utilization of virtual reality technologies enables students to develop the requisite skills to service CNG filling station pumps, undertake troubleshooting, and comply with safety procedures at the facility.
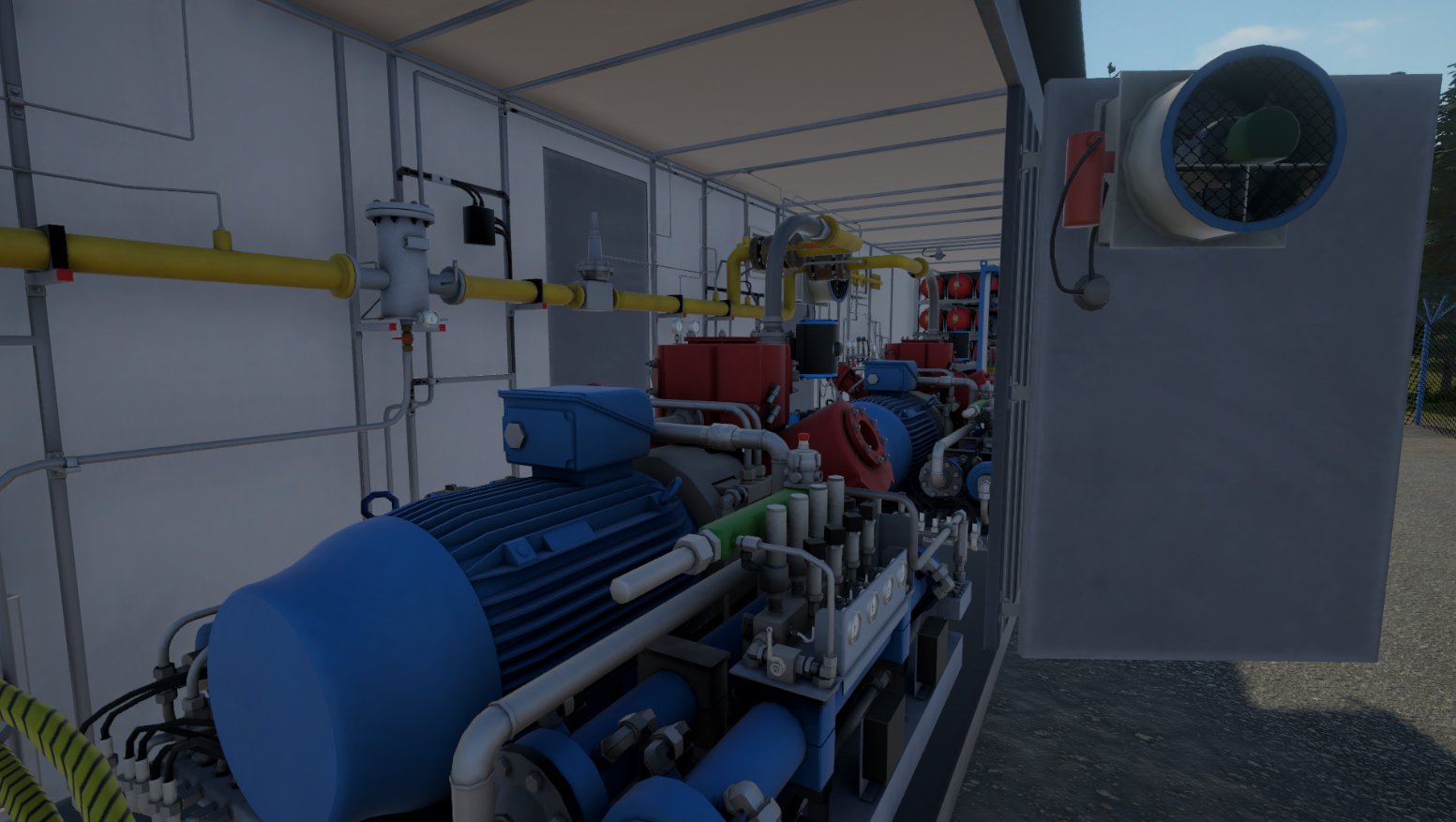
The compressor equipment of CNG filling stations is designed to be continuously operational. Any deviation from this mode is highly undesirable and infrequent, such as when the emergency stop mode is engaged. The utilization of a virtual simulator represents the optimal methodology for the training of personnel in the requisite response to emergency situations.
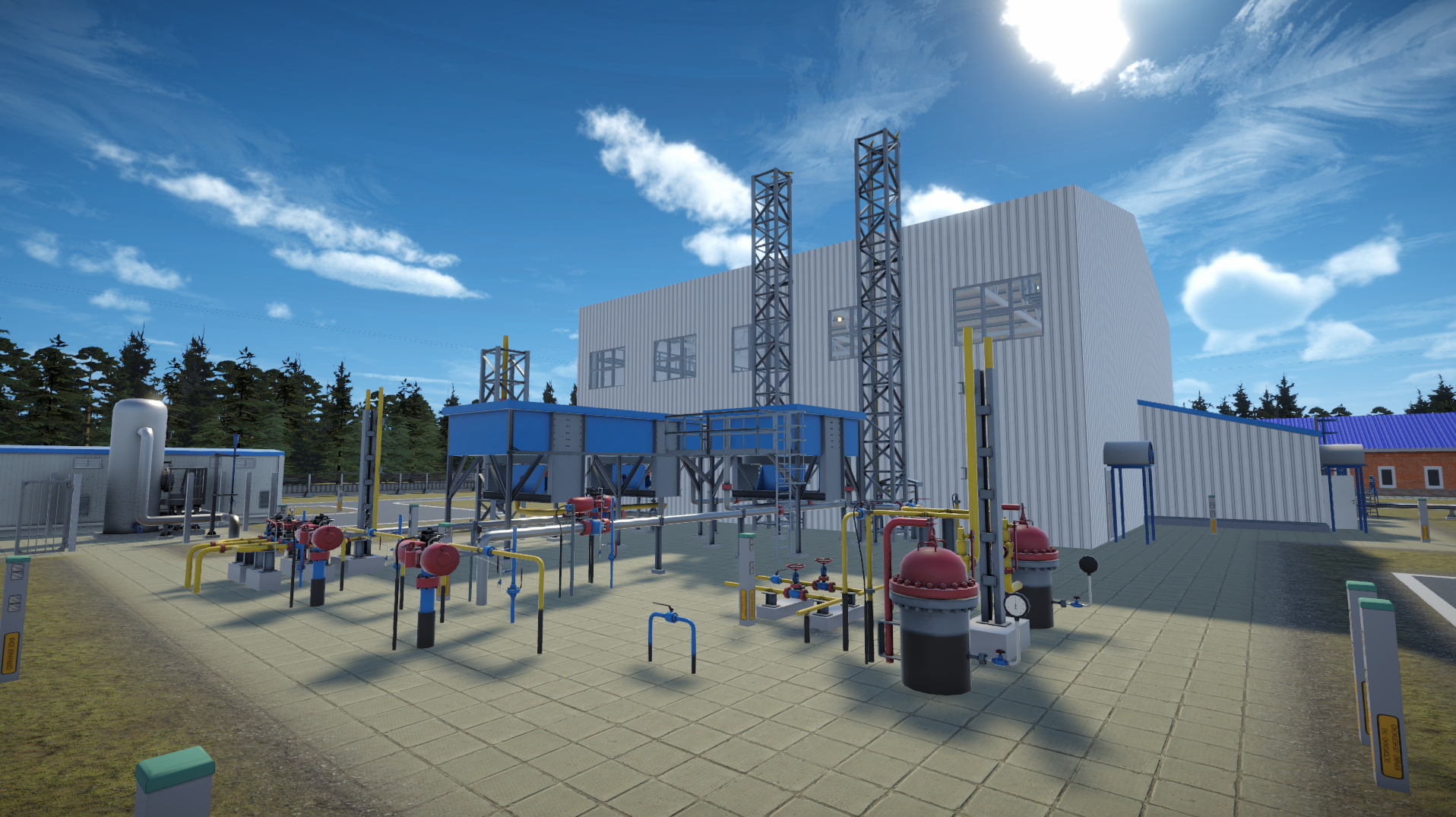
The digital models reproduce the primary components and architectural design of the Gazprom Gazomotornoye Toplivo real facility: CNG filling station-22 in St. Petersburg. The most comprehensive equipment of the gas block container has been developed, comprising a block for connecting to the city main gas network (pressure 1.2 MPa), a dehydration system, gas cylinder systems for storing compressed natural gas, air cooling devices, six fuel dispensers, and other components.
Virtual training sessions are based on the technological regulations, bypass routes, and actions of shift operators at CNG filling station-22.
The system is prepared in two versions, one for use with the VR headset and manipulators, the other for keyboard and mouse control.
‘The utilization of contemporary virtual reality simulators is of paramount importance in the training of professionals specializing in the fuel and energy sector. Such technology enables the elimination of the risk of injury during training while simultaneously modeling dangerous situations that may occur at facilities. Students who have undergone training on VR simulators demonstrate enhanced proficiency and knowledge regarding equipment operation, as well as a more rapid adaptation to their work environments,’ said Alexander Drozdov, Professor of the Higher School of Power Engineering at the SPbPU Institute of Energy.